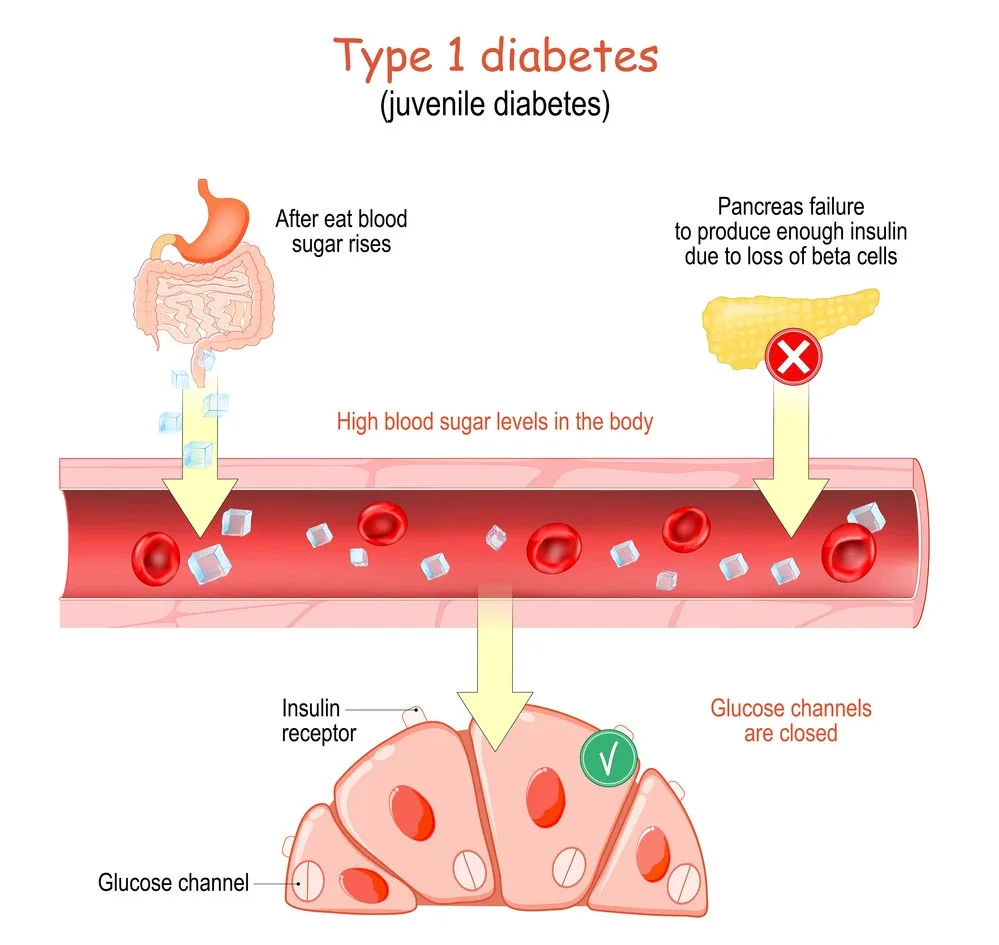
Type 1 diabetics can eat everything as long as they do enough insulin. The amount of insulin needed depends on the carbohydrate content in their meal. However, you can eat whatever you want! It’s tempting to think that more carbs are better if some carbs are bad. But this isn’t true; it’s important to moderate your carb intake across the day and week so that your blood glucose remains within normal limits at all times.
Things you can eat with type 1 diabetes

If you have type 1 diabetes, you can eat whatever you like. However, if you eat too much of something that raises your blood sugar level, such as a large serving of pasta or rice with sauce and meatballs, your body will need extra insulin to compensate for this rise in blood sugar.
People with type 1 diabetes must be very aware of the number of carbohydrates consumed at meals. They also need to know how to calculate their insulin doses (for example: how many grams of carbohydrate are in a particular food item?). The different types of carbohydrate content include:
- Starch
- Sugars
- Fiber
The amount of carbohydrates in food is measured in grams (g). The glycemic index is a measure that indicates how quickly and how much your blood sugar level rises after eating a particular food. The higher the GI value, the faster your blood sugar level increases.
What foods should type 1 Diabetic avoid?

In general, type 1 diabetics should avoid eating foods high in fat, sugar, and salt. They also should avoid foods high in carbohydrates, protein, and fiber. Examples of these types of foods include:
- Foods containing saturated fats, such as red meats, butter, and coconut oil
- Foods containing trans fats, such as margarine and some processed or fried foods
- Foods containing refined sugars, such as cakes, chocolates, and pastries
- Foods containing polyunsaturated or monounsaturated fats (i.e., vegetable
oils)
- Protein-rich foods like meat products (including poultry), eggs, fish (like salmon), beans/legumes/pulses
Understanding carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are sugars and starches. They’re the main source of energy for the body, and they’re broken down into glucose. Glucose is stored in the liver and muscles as glycogen, which can be converted to fat.
The total daily carbohydrate amount you should eat depends on your activity level and body size. If you exercise regularly or are very active, you should consider eating more carbohydrates than someone who is sedentary. The number of carbohydrates you eat should not exceed your target intake from your meal plan based on these factors:
- Body size (small, medium, or large)
- Activity level (low, moderate, or high)
If you’re a small person who exercises regularly, your target intake may be between 130 and 225 grams daily. If you’re a medium-sized person who is passive and moderately active, your target intake might be between 175 to 275 grams per day. And if you are large and very active, your target intake could be as high as 400 grams per day.
How to enjoy a type 1 diabetes diet?
- Eat a balanced diet

People with type 1 diabetes eat regular meals and snacks daily to keep their blood glucose levels steady. To ensure you eat enough calories for your activity level, use our Calorie Calculator to find how many calories you should eat.
- Check blood glucose levels regularly.

Test before meals, after meals, and at bedtime to help prevent low blood sugars (hypoglycemia). If testing isn’t convenient, use an online tool like Livongo Health AI or Accu-Chek Aviva Connected Meter. In addition, using these tools means fewer finger pricks for all users, reducing pain and stress levels for those with chronic illnesses like diabetes!
- Make healthy food choices.

Choose foods higher in fiber than those low in fiber; complex carbohydrates provide long-lasting energy without spiking insulin levels too much, while simple carbohydrates cause rapid spikes followed by crashes later on down the road – just like sugar does when consumed without moderation!
Things you can eat for breakfast
Your daily meals should be a healthy mix of proteins, carbohydrates, and fats.
- Protein can come from lean meats like chicken breast, turkey, and tuna fish.
- Carbohydrates are found in grains, like whole-wheat bread and brown rice.
- Fats are found in dairy products such as cheese or milk (but be wary of too many saturated fats).
- Consider adding oatmeal or whole grain cereal into your diet since carbohydrates turn into glucose, which your body uses for energy.
If you don’t have time to cook every morning before work or school—or if cooking isn’t something you feel comfortable doing—then look for prepackaged breakfast foods that contain protein and carbohydrates at the grocery store instead!
Conclusion
This question is very common, and the answer is yes! Type 1 diabetes patients can eat whatever they want. But it’s important to understand that your blood glucose levels will fluctuate throughout the day, so that you may need more insulin than usual. This may be due to things like exercise or even eating certain foods. So you must have enough insulin on hand at all times so that you don’t find yourself in trouble when these situations arise!



Leave A Comment