Is there a cure for adult-onset gigantism?
Houston Endocrine Center2023-02-24T13:18:22+00:00Have you noticed that your height has been increasing for no apparent reason? Do you find yourself growing faster than your peers? If so, it may be time to get a diagnosis for adult onset gigantism.

However, before we talk about the treatment options available to you, let’s take a closer look at this condition and why it occurs in adults.
Gigantism

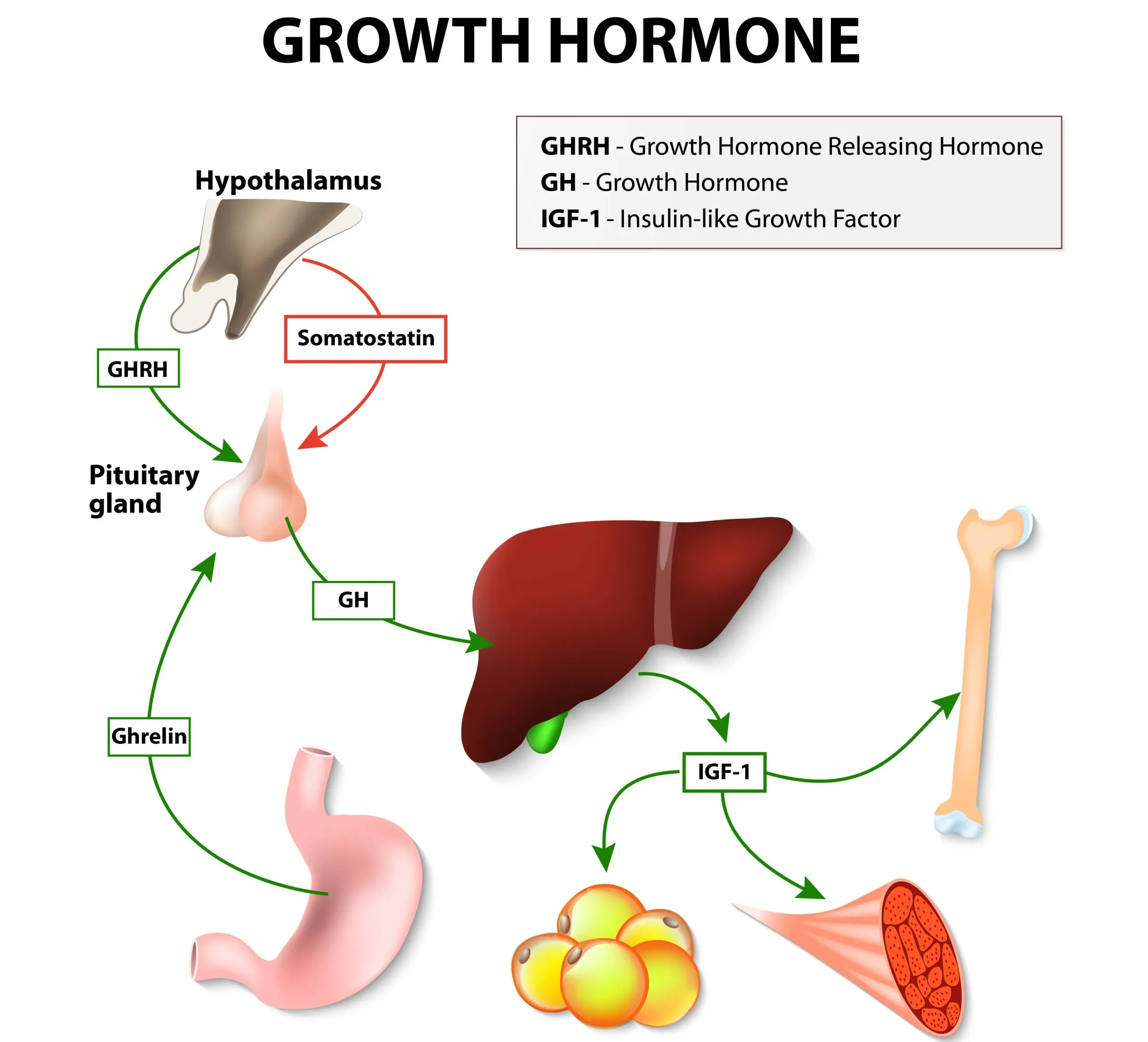
Gigantism is a rare condition that causes fast, abnormal growth in children. The growth occurs due to the overproduction of human growth hormone (HGH), which happens when the pituitary gland secretes more of this hormone than normal.
The syndrome is also known as acromegaly or macrosomia. This condition affects 1 in 100,000 people worldwide and can occur at any age but most commonly affects adults who are 20-40 years old.
A tumor causes it on the hypothalamus or pituitary gland, which releases excessive amounts of HGH into your bloodstream. This hormone stimulates bone cells to grow faster than usual, causing your bones and organs to enlarge beyond what’s normal for your body type or height—which explains why many people with gigantism have abnormally large hands, feet, and heads!
What are the signs and symptoms of gigantism?

The signs and symptoms of adult-onset gigantism include:
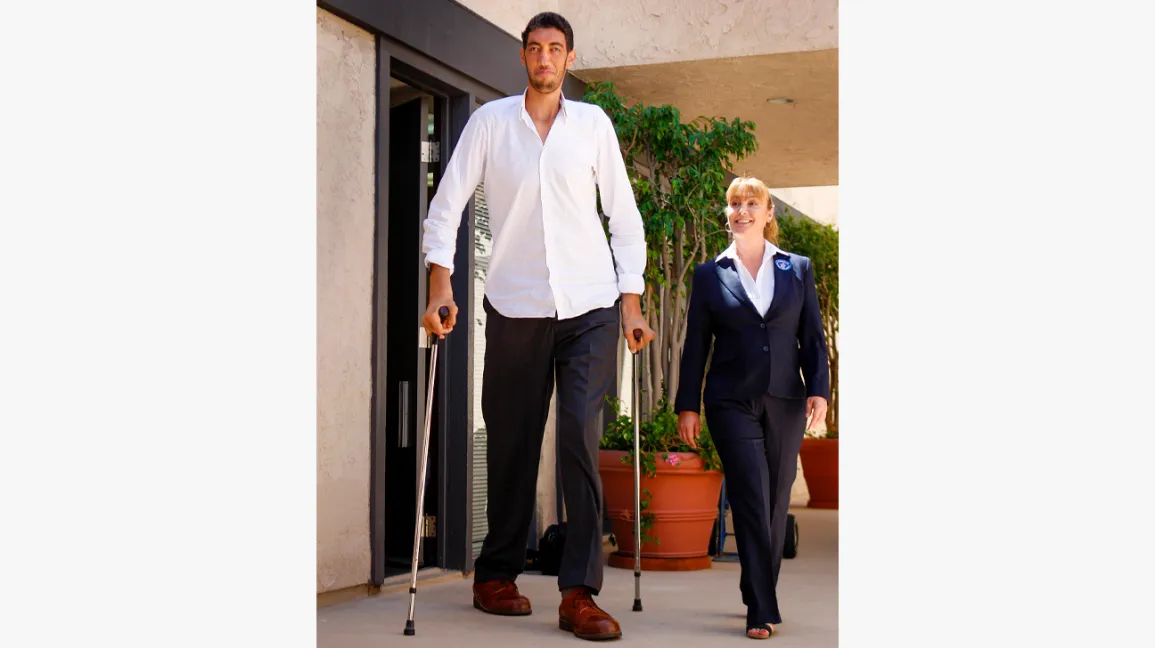
- Increased height: If left untreated, gigantism can lead to symptoms such as an increased length of your legs, which means that you may have trouble walking on your own. In addition, the condition can cause a bigger head and neck, making it difficult for you to turn around or bend.
- Muscle weakness: The condition prevents muscles from developing properly, and this causes issues like having trouble carrying groceries or lifting heavy objects off the ground without assistance. It also leads to problems with joints because they aren’t strong enough to support your body’s increased size; this results in back pain when sitting for too long or arthritis when standing up after sitting down for an extended period (like during class).
- Joint problems: Due to weak bones supporting them, joints tend not to be able to take as much weight as they should; this causes pain when walking around town where there’s more pavement than grassy knolls nearby! You might even notice swelling after spending hours working out each day at home – especially if those exercises involve lifting weights above head level rather than just doing squats behind closed doors.
The condition can also cause fatigue and exhaustion, making it difficult to complete normal tasks like shopping or taking care of your kids. Plus, if you aren’t sleeping well at night due to back pain or joint issues, you’ll have even more difficulty concentrating on what your instructor says during class!
How is gigantism diagnosed?
- Physical exam
- X-ray
- Blood tests
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) or CT scan (computerized tomography).
How is gigantism treated?
Treatment depends on the type and severity of gigantism. For example, children with mild growth hormone-producing tumors can be treated with medication that reduces the activity of these hormones. If surgery is necessary, it may be used to remove a tumor or reduce pressure on one side of the brain by removing a portion from the skull. Radiation therapy and chemotherapy are also sometimes used to treat adult-onset gigantism and other pituitary tumors resulting from excess growth hormone production.
Surgery for gigantism
Surgery for gigantism is a last resort and involves removing the excess bone tissue and cartilage in your bones. Surgery has risks, including infection, nerve damage, and complications with anesthesia. Surgery does not always correct all the physical effects of gigantism, so it’s important to discuss all potential outcomes before undergoing any procedure.
Your insurance may cover the surgery if you have been diagnosed with gigantism and meet the medical criteria for treatment. Your healthcare provider will help determine whether or not you qualify for this coverage by looking at factors such as age and other medical conditions that could affect the procedure’s success rate and its cost-effectiveness compared to alternative treatments like medication or physical therapy sessions.
If surgery is recommended, it’s best to get a second opinion from another doctor. You can also look into the pros and cons of surgery with your insurance provider or financial advisor before deciding whether or not to proceed.
It’s also important to consider how gigantism affects you and your family. If you have children, they may be more likely than their peers to be bullied, teased, or harassed by classmates. This could lead to emotional problems later in life.
Radiation therapy for gigantism
Radiation therapy is a treatment for bone tumors and cancer. You may be thinking, “Wait, what? Don’t we want to shrink the tumor?” Well, there are two different ways to do this: shrinking the tumor before surgery or shrinking it after surgery.
In either case, radiation therapy is used to kill cancer cells. In some cases where you have an adult onset gigantism tumor that has grown large enough that it needs to be removed surgically (removed), radiation can help shrink your tumor before surgery so that your surgeon has less of a job on their hands when they take out your tumor.
This means that if you decide on having surgery as your treatment method for adult-onset gigantism, radiation therapy can also help reduce pain post-surgery by killing any remaining cancer cells in your body which could delay recovery time if left alone and make healing more difficult.
What are the possible complications of gigantism treatment?
The complications of any treatment for gigantism will depend on the treatment. Here are some examples:
- Surgery to remove a pituitary tumor can result in bleeding or infection. It may also be difficult to control the swelling caused by removing the pituitary gland, leading to headaches and pain behind the eyes. Surgery can cause permanent damage to nerves that supply vision in rare cases.
- Treatment with growth hormone can cause fluid retention (edema) in your hands and feet, high blood pressure (hypertension), glucose intolerance (a disorder that affects how your body handles sugar), immune deficiency syndrome, and osteoporosis—a condition where bones become weak and break easily due to lack of calcium or vitamin D deficiency—among others.
Conclusion
For the most part, gigantism is a disease that can be treated and managed. Surgery and radiation therapy are effective at controlling the symptoms of this condition. However, some risks associated with these treatments should be considered before starting any treatment plan.