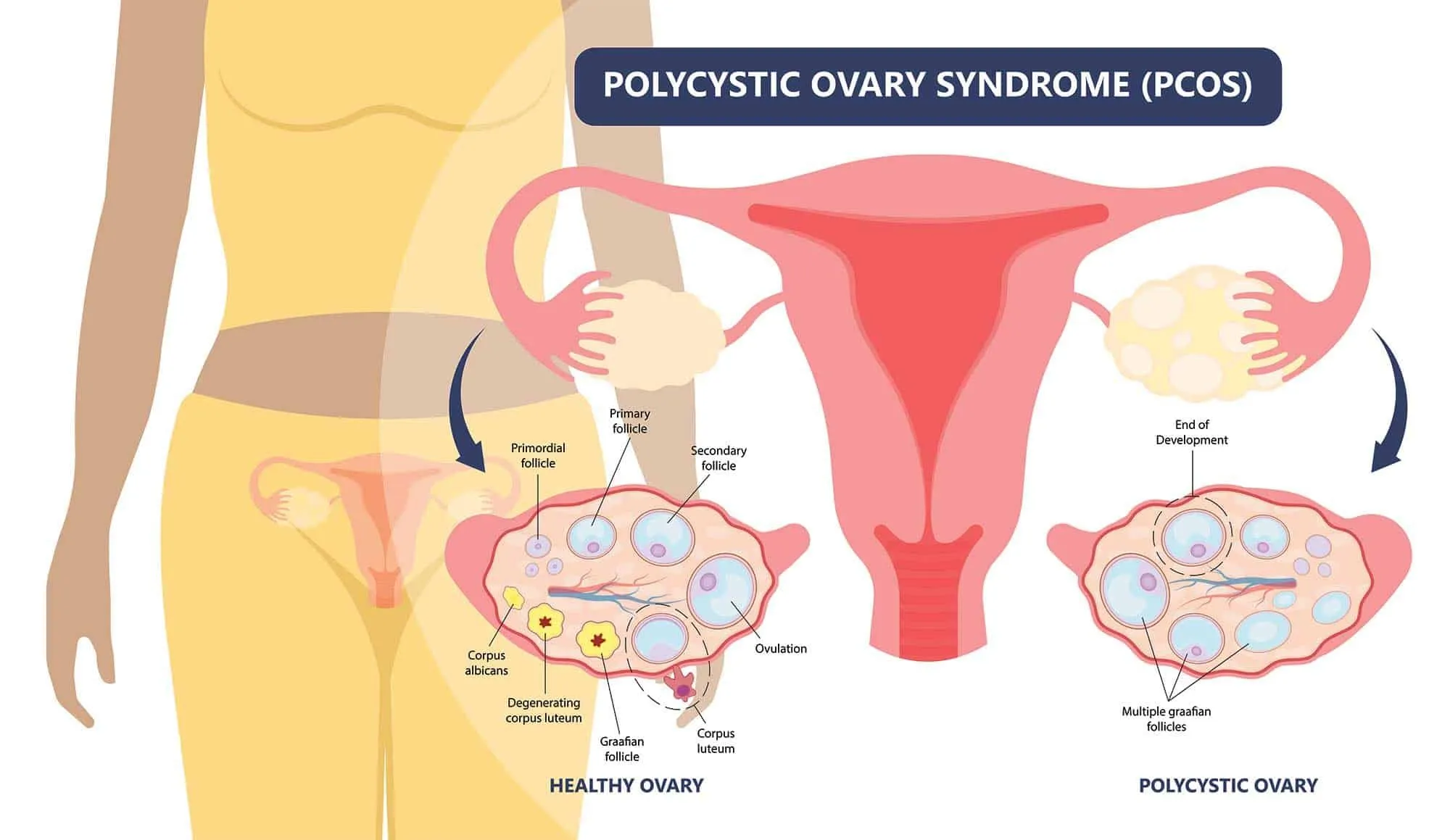
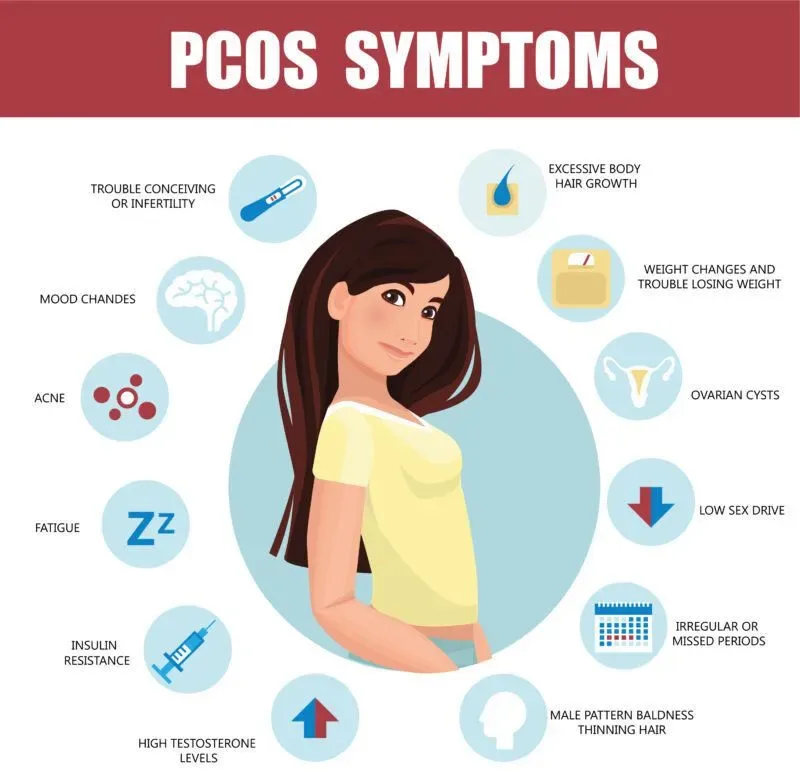
Hirsutism is a condition that affects women and causes hair to grow in places where it’s typically not found in women. It can affect your face, arms, and chest, as well as your pubic area. The hair can be thick and dark or thin and light. Some women have only a few patches of excess hair, while others have more extensive patches all over their bodies. In rare cases, hirsutism can cause male-pattern baldness in women who were born female but who genetically are male due to an abnormality with their Y chromosomes (also called Klinefelter syndrome). If you’re concerned about hirsutism, talk with your healthcare provider about whether more testing is needed based on how severe your symptoms appear. They’ll also be able to discuss possible options for treatment if needed.
Diagnosis of hirsutism
A doctor diagnoses hirsutism. It can be measured using the Ferriman-Gallwey scoring system, which scores your hair growth from 0 to 4.
- A score of 0 or 1 indicates that you have no hirsutism and are unlikely to have any problems with it.
- A score of 2 indicates that you have mild hirsutism that may cause some concern but won’t cause major issues in daily life or affect your fertility if left untreated; however, it’s still important to see a doctor for further evaluation and treatment options if needed.
- A score of 3 indicates moderate to severe symptoms such as increased facial hair growth (beard) or chest hair (mammary hypertrophy) along with other signs such as male pattern baldness at an early age for women who don’t normally experience this type of hair loss before menopause takes place naturally over time regardless whether she has undergone chemotherapy treatments first before then later developed into male pattern baldness after getting cancer again later down the road due too late diagnosis.
How is Hirsutism Typically Treated?
Hirsutism is typically treated with drugs, laser therapy, and surgery.
Drugs such as spironolactone block the action of male hormones in the body. These medications may be effective for some women but can have side effects such as nausea and fatigue.
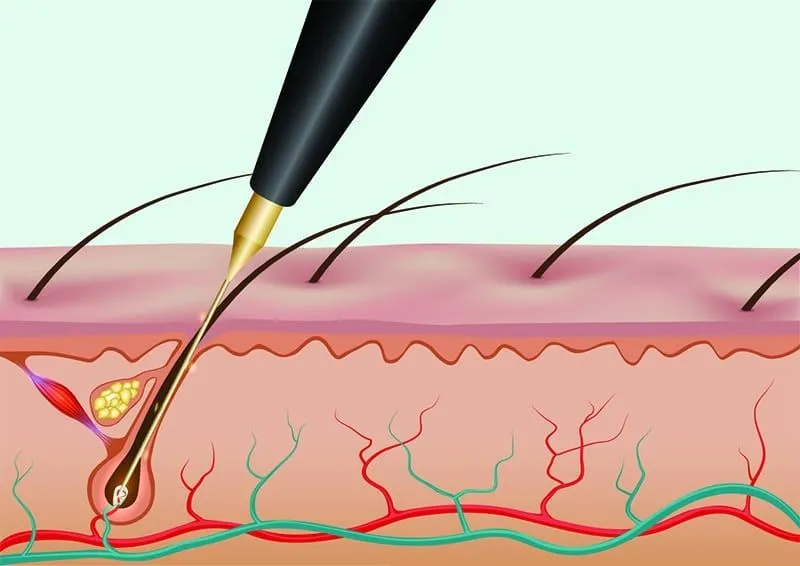
Laser therapy involves applying heat energy to hair follicles to destroy them so they do not grow. A dermatologist often performs this treatment with sedation (a general anesthetic) at a clinic or hospital setting. You must speak with your doctor about any possible risks before undergoing laser hair removal procedures, as they vary depending on what type will be used on you!
In addition to these options, there are also natural methods such as diet changes which include eating foods high in protein which helps boost metabolism, while avoiding those rich in carbohydrates which can cause weight gain over time if eaten excessively during meal times each day.”
Medical treatment for hirsutism
Hirsutism is a common condition and can be caused by several factors. It’s not life-threatening but can be treated with medications or natural methods.
Medical treatment is often recommended when the symptoms are severe and have been present for a long time. Treatment aims to reduce hair growth on the face, chest, and back by suppressing hormone production in the ovaries or testes (or both). The most common drugs used are spironolactone (Aldactone) and cyproterone acetate (Androcur). In addition to these medicines, laser therapy is sometimes used on areas with thick hairs, such as the backs of hands or forearms. This can help prevent ingrown hairs from developing into infections like boils/abscesses, which often form after shaving off unwanted facial hair.
Nutrition and Dietary Supplements
- Vitamin E and zinc: All these vitamins are related so you can combine them.
- Iron and selenium: Both are essential for proper hair growth in women suffering from PCOS or hirsutism.
- Vitamin B6 and B12: This two help reduce the amount of testosterone produced by the body, which is why they are good for treating hirsutism caused by PCOS or any other condition that causes increased levels of this hormone in your system (like obesity).
- Folic acid is another important nutrient because it helps increase blood flow to the scalp, promoting healthy hair growth! Plus, it helps prevent premature graying, too – bonus!
- Omega 3 fatty acids/vitamin D3/calcium: All three help reduce inflammation within your body while also improving circulation throughout your entire system; this helps keep everything working smoothly so that nothing gets blocked up like veins or arteries could become if left untreated long enough without treatment options available like surgery procedures done by qualified surgeons who specialize only in operations involving those areas where there might be blockages due out there somewhere deep inside our bodies.”
Herbs
Herbal remedies are a great way to treat hirsutism. Herbs can help balance hormones and improve other symptoms of PCOS, such as weight gain and hair loss.
Herbs for Hirsutism:
- Saw Palmetto – This herb has been used for centuries to treat urinary problems, including frequent urination (polyuria). It’s also used for prostate enlargement (benign prostatic hyperplasia), which may cause difficulty urinating or a slow urine flow. Saw palmetto extract contains fatty acids that reduce inflammation in the prostate gland and help prevent fluid retention caused by high blood pressure medications such as ACE inhibitors or diuretics like hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ).
Saw palmetto

Saw palmetto is a popular herbal treatment for hirsutism. It can help reduce hair growth, lower the level of dihydrotestosterone (DHT) in the body, and increase the amount of estrogen in women with too much testosterone.
The best way to take saw palmetto is by swallowing capsules or tablets that contain standardized extracts from this plant’s berries or leaves. Before expecting results, you should take at least 320 mg daily over three months.
Chaste tree

Chaste tree, also known as Vitex agnus castus, is an herbal remedy that can help with hirsutism. It’s a tonic for the pituitary gland and helps regulate thyroid function and adrenal issues related to hormone balance.
Black cohosh

Black cohosh is a herb used for centuries to treat menopausal symptoms. It is thought to help balance estrogen and progesterone levels, which may be why it is effective at treating hirsutism in some women. However, there are no clinical trials on its effectiveness as a treatment for hirsutism.
Black cohosh should not be taken while pregnant or breastfeeding because it can cause uterine contractions and increase bleeding during menstruation.
Spearmint tea

Spearmint tea is another natural remedy for hirsutism, which can be used to treat it. It has been found that spearmint contains high amounts of carvacrol, an oil that helps in reducing the production of male hormones like testosterone and DHT (dihydrotestosterone).
The best part about spearmint tea as a treatment option is that it’s easily available at home or any health store near you. You don’t need any prescription from your doctor, either!
Acupuncture

Acupuncture is one of the most popular forms of alternative medicine worldwide. It’s used to treat various conditions, including pain and stress-related disorders. Acupuncture may also be helpful for hirsutism because it can help reduce your body’s production of testosterone (a hormone that causes hair growth).
While acupuncture has been used safely for thousands of years, you should talk to your doctor before trying it on yourself or someone else. If you try this natural treatment option, ensure that your acupuncturist is licensed by the state where they practice; many states require this certification before allowing anyone to practice acupuncture within their borders.
Eat a Blood Sugar Balancing Diet
A blood sugar-balancing diet helps to regulate your insulin levels. A diet high in refined sugars and carbohydrates can cause spikes in insulin, which leads to an increase in androgens (male hormones) and hair growth in the body.
To avoid this, you should eat a diet low in refined sugars, carbohydrates, and saturated fats. Instead, focus on eating more protein (like lean meat or fish), good fats (like olive oil), vegetables, fruits, whole grains, oats, etc. Don’t eat too much dairy or soy products because they contain phytoestrogens which can cause an imbalance of estrogen levels and increase hair growth! In addition, don’t drink too much alcohol either, as this can lower testosterone levels leading to an increased risk for hirsutism!
Try Inositol to Support Blood Sugar
Inositol is a B vitamin that can help balance blood sugar, support healthy hair growth, and prevent hirsutism. It’s also known as myoinositol or D-chiro-inositol.
Inositol benefits people with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), which causes irregular periods and excess body hair in women. A study published in “Fertility and Sterility” found that taking 2 grams per day of D-chiro-inositol improved the symptoms of PCOS by reducing testosterone levels, insulin resistance, and ovarian hormone production.
Inositol hexaphosphate (IHP), another form of this compound found naturally in food sources such as fruits, beans, and nuts — but not necessary if you’re eating well! — may also help reduce male pattern baldness by slowing down hair loss due to its antiandrogenic effects on male hormones such as dihydrotestosterone (DHT)
Use Vitex for Better Hormone Balance
Vitex is a plant that helps balance hormones. It can be used to treat hirsutism as it regulates the production of testosterone and other male hormones.
How To Use Vitex:
- You can use Vitex in three ways: by consuming it as tea or juice, taking pills, or using the cream on your skin. The latter is preferable since you can apply it directly on the affected areas, such as your face, neck, and back, where hair grows excessively thickly due to high levels of DHT (a hormone responsible for male characteristics).
Conclusion
Hirsutism is a common condition that can affect women of all ages. It can lead to embarrassment and anxiety, but there are many ways to treat it. If you have been diagnosed with hirsutism or know someone with this condition, please share this article with them so they can find some relief from their symptoms!