
Under certain circumstances, the surgical removal of half of the thyroid gland, known as a thyroidectomy, may be necessary. This procedure is typically performed to treat thyroid nodules, goiter, or thyroid cancer. After undergoing a thyroidectomy, it is natural to wonder what changes and adjustments lie ahead. This article will explore what you can expect after removing half of your thyroid, including the impact on hormone levels, potential symptoms, and necessary follow-up care.

Hormone Levels and Medication:
After removing half of your thyroid, hormone levels may be adjusted, particularly in producing thyroid hormones. The remaining portion of the thyroid gland may compensate for the loss, but in some cases, hormone imbalances can occur. To manage this, your doctor may prescribe synthetic thyroid hormone medication, such as levothyroxine, to help regulate hormone levels and ensure the proper functioning of your body’s metabolism.
Potential Symptoms:
While many individuals experience a smooth transition after a thyroidectomy, it is important to be aware of potential symptoms that may arise during the recovery process. These symptoms can include ,
- Temporary fatigue
- Muscle weakness
- Weight changes
- Hair loss
- Dry skin
- Sensitivity to cold or heat
- Mood fluctuations.
Communicating any persistent or concerning symptoms to your healthcare provider for further evaluation and guidance is crucial.
Scar Healing and Recovery:
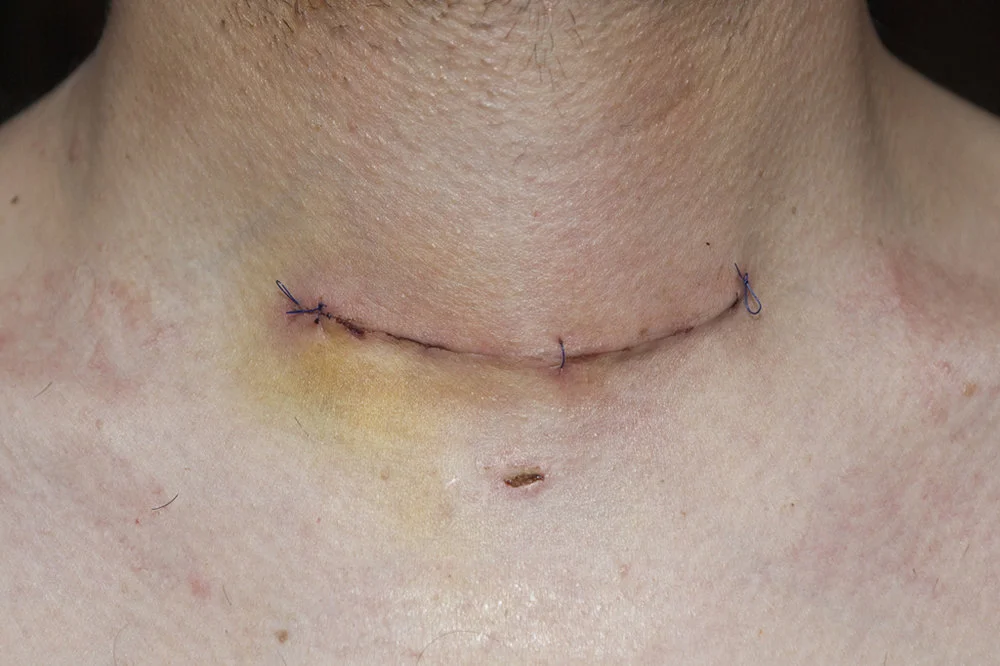
A thyroidectomy involves a surgical incision in the front of the neck. After the procedure, it is normal to experience some swelling, bruising, and discomfort in the surgical area. Your surgeon will provide instructions on wound care and how to minimize scarring. Over time, the scar will gradually fade and become less noticeable. Following post-operative care instructions and attending scheduled follow-up appointments is essential to ensure proper healing and recovery.
Lifestyle Adjustments:
Although a thyroidectomy does not significantly impact daily activities for most individuals, certain lifestyle adjustments may be necessary. Maintaining a healthy and balanced diet is important to support overall well-being and manage potential weight changes. Regular exercise and physical activity can also contribute to maintaining a healthy weight and improving energy levels. Also, managing stress and practicing self-care techniques can be beneficial during recovery.
Ongoing Monitoring and Follow-up Care:
After a thyroidectomy, regular monitoring and follow-up care are essential. Your healthcare provider will schedule periodic check-ups to assess hormone levels, adjust medication dosage, and monitor potential complications. These follow-up appointments also allow one to discuss concerns, ask questions, and receive guidance regarding long-term management and lifestyle adjustments.
Here are some common aspects of ongoing monitoring and follow-up care after a thyroidectomy:
Hormone Level Assessment:
Regular monitoring of thyroid hormone levels is essential to ensure your body maintains a proper balance of thyroid hormones. This typically involves periodic blood tests to measure levels of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), free thyroxine (FT4), and possibly triiodothyronine (T3). The frequency of these tests may vary initially, but they are generally conducted every few months until your hormone levels stabilize. Your healthcare provider may adjust your thyroid hormone replacement medication dosage based on the results.
Medication Adjustment:
If you are taking synthetic thyroid hormone medication, such as levothyroxine, regular follow-up appointments will allow your healthcare provider to assess the effectiveness of the medication and make necessary dosage adjustments. The goal is maintaining thyroid hormone levels within the target range to support optimal metabolism and overall well-being.
Physical Examination:
During follow-up visits, your healthcare provider will execute a physical examination to assess the surgical site, check for any signs of swelling or abnormal growth, and evaluate overall thyroid function. They may also palpate the neck area to identify unusual lumps or nodules.
Imaging Studies:

In some cases, imaging studies such as ultrasound or radioactive iodine scans may be recommended to evaluate the remaining thyroid tissue, monitor for the presence of any residual or recurrent thyroid nodules, or detect any signs of thyroid cancer recurrence.
Cancer Surveillance:
Ongoing monitoring for cancer recurrence is essential if your thyroidectomy was performed due to thyroid cancer. This may involve regular blood tests, imaging studies, and potential consultation with an endocrinologist or oncologist specializing in thyroid cancer management. Your healthcare provider will determine the appropriate surveillance plan based on your situation and cancer stage.
Long-term Lifestyle Management:
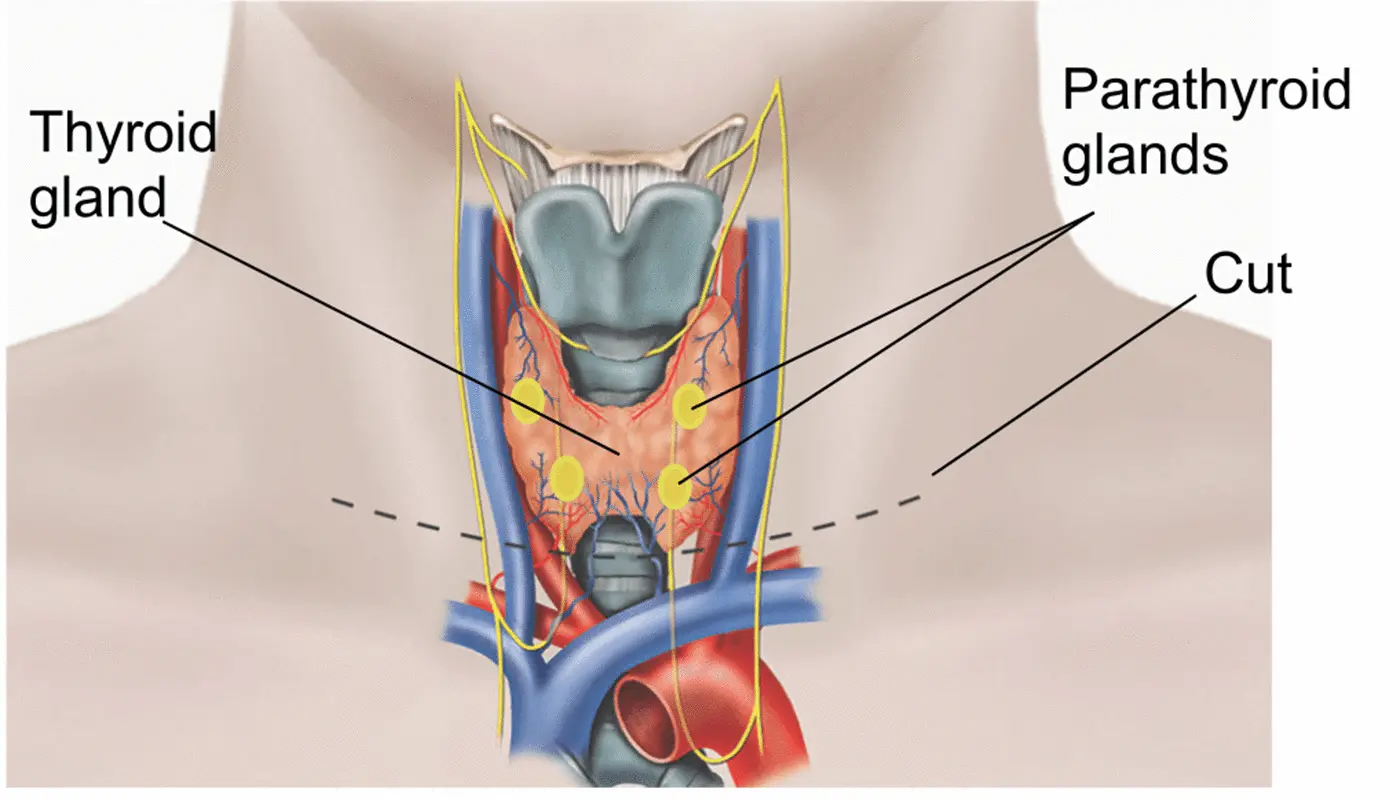
Following a thyroidectomy, it is vital to maintain a healthy lifestyle and make certain adjustments as needed. This includes regular exercise, a balanced diet, stress management, and adequate sleep. Your healthcare provider may offer guidance on dietary considerations, weight management, and potential calcium or vitamin D supplementation if the surgery involves the removal of parathyroid glands.
Communication and Education:
Effective communication with your healthcare provider is crucial throughout the follow-up care process. Your healthcare provider can address your questions, provide education about long-term management, and guide you on self-care practices. It is important to report any symptoms, concerns, or changes in your health during follow-up visits.
Remember, each individual’s specific monitoring and follow-up care plan may vary. It is crucial to follow the recommended schedule of follow-up appointments and maintain open communication with your healthcare provider to ensure optimal care and management after a thyroidectomy.
Emotional Support and Education:
Going through a thyroidectomy can be an emotionally challenging experience. It is important to seek support from family, friends, or support groups to share your feelings, experiences, and concerns. Education about the thyroid gland, its functions, and the impact of thyroid hormone imbalances can empower you to understand your body better and actively participate in your care.
Conclusion:
Undergoing a thyroidectomy, which involves the removal of half of the thyroid gland, may require adjustments and adaptations in your daily life. Most individuals can lead healthy and fulfilling lives after the procedure with appropriate medical care, monitoring, and lifestyle adjustments. Regular communication with your healthcare provider, adherence to medication, healthy lifestyle practices, and emotional support can contribute to a smooth recovery and overall well-being. Remember, every individual’s experience may vary, and it is crucial to consult your healthcare provider for personalized guidance and support throughout your thyroidectomy journey.



Leave A Comment