Why is diabetes education important for every individual?
Houston Endocrine Center2022-12-26T13:24:49+00:00Diabetes is a very common disease in the world. It is a group of diseases where the body cannot produce enough insulin or use it properly. The main problem caused by this disease is that blood sugar levels increase and become too high, which leads to serious health problems if not treated properly. Nowadays, diabetes education is taught to everyone because it can be very helpful for people suffering from this condition. There are many different types of diabetes; however, most share some similarities. Let’s take a look at some reasons why diabetes education is important for every individual:
Diabetes management and the role of education
Diabetes education is important for everyone, not just people with diabetes. The goal of diabetes education is to prevent diabetes complications and improve the quality of life for diabetics. It’s also helpful for family members and caregivers living with someone with type 1 or 2 diabetes.
Diabetes can be managed through healthy eating, physical activity, and self-care. By working with a healthcare team that includes your doctor, dietitian, and pharmacist, you can learn how to manage your condition to live a long, healthy life free from complications caused by blood sugar levels.
Understand which foods are good for the body and which are not.
It is important to understand which foods are good for the body and which are not.
If you want to stay healthy, you must eat a balanced diet. The goal is to get 45-65% of your calories from carbohydrates, 10-35% from fats, and 15-30% from protein.
To achieve this, it is recommended that you eat more fruits and vegetables (vegetables have more fiber than fruits), less sugar and salt, and less saturated fat (the kind that comes from animal products) but more whole grains. You should also eat more protein, like beans or nuts, to stay strong while losing weight through exercise!
Make sure not too much fat goes into your body by reducing the number of processed foods such as potato chips or sugary drinks like soda pop because they contain lots of trans fats, which can lead to heart disease if consumed regularly.
Improve eating habits and increase exercise
To prevent diabetes, you need to change your eating habits and increase physical activity. This can be challenging for many people who have busy schedules and live in a fast-paced world. The key is to make small changes over time that can lead to big results.
- Eat healthily by choosing less sugar and fatty foods, such as vegetables, whole grains, fruits, and nuts.
- Increase your physical activity by doing something active daily (such as walking the dog or doing a quick jog). It doesn’t have to be hard — do whatever feels comfortable!
Control the blood sugar level with medication, insulin, or other approaches.
- Take your medication regularly.
- Use insulin as directed by your doctor and keep it out of the reach of children.
- Be aware of how much sugar is in foods and drinks. If unsure, check the food package label or ask the restaurant’s servers.
- Watch out for hidden sugars in food products such as bread, cereals, and salad dressings. Check the ingredients list on labels for words ending with “ose” (e.g., dextrose) or “syrup” to find added sugars in processed foods like peanut butter and canned soup; these will increase your blood sugar level quickly if you eat too much of them at once without any other carbohydrate source present to slow down absorption from your digestive system into circulation where it can raise fasting glucose levels.
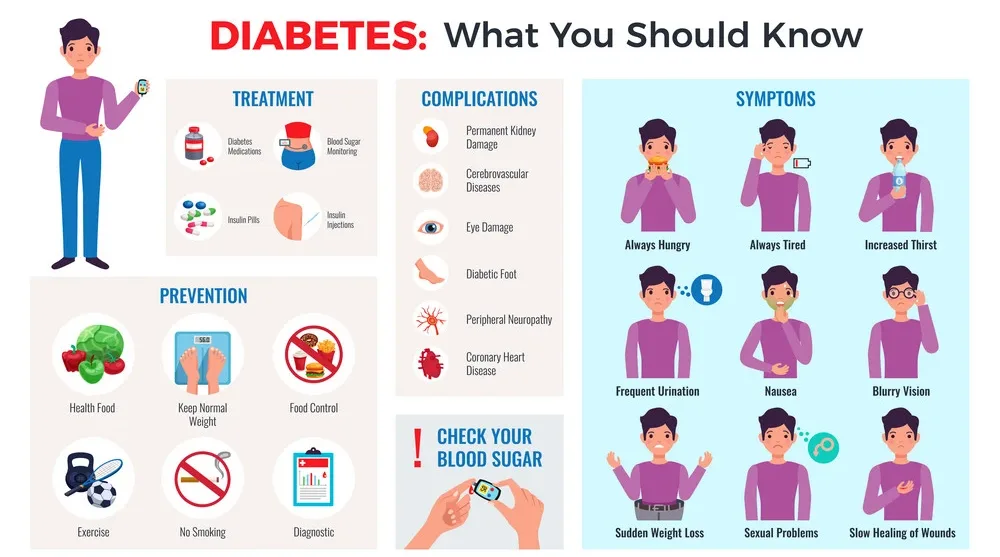
Identify the symptoms when something is going wrong and what to do.
For many people, diabetes can be a scary and confusing illness. If you have diabetes but don’t know what to do or how to handle it, you must educate yourself about the disease to ensure a healthier future. Here are the common symptoms of diabetes:
- Increased thirst
- Increased urination
- Weight loss without trying
- Blurred vision or blindness
- Pain in the eyes or feet
- Rapid heart rate
- Increased hunger
- Fatigue or feeling tired
- Itching around the eyes and mouth
Learn how to manage stress and worry
Once you are aware of what to look out for, you can take measures to reduce the stress in your life. This might include:
- Learning how to manage your time, so you don’t overcommit yourself and feel overwhelmed.
- Practicing meditation or deep breathing exercises regularly.
- Spending good time with people who make you happy instead of those who bring out the worst in you.
If these things aren’t enough to manage your stress levels, consider seeing a doctor or psychologist who can recommend other solutions best suited to your situation.
Diabetes education is key to a healthy life.
With diabetes education, you can live a healthier life.
Diabetes education is key to a healthy life. The importance of diabetes education cannot be overlooked in the modern healthcare system.
It provides an opportunity for individuals to become well-informed about their disease and acquire skills that will help them make informed decisions about their treatment options and lifestyle changes that may affect health outcomes. People with diabetes are not limited to just one type of education—there are many avenues through which they can receive information about managing their condition effectively:
- Classroom-based learning, such as lectures or group sessions with doctors or nurses
- Online resources such as websites/websites (web sites/websites) that offer interactive features such as quizzes, tips on how best manage your diet, tips on how best manage your diet, etc., e-books (e-books), podcasts (podcasts), videos (videos), blogs (blogs).
Conclusion
Diabetes education is very important for every individual in society. Individuals with diabetes should be aware of the disease and how to deal with it. The education centers are available in many places so that people can get the information easily and eliminate this problem.
