
Source: Open Book
Ever wonder why you perceive everything the way you do? You look at a red apple, for example, and see it as red. You then compare that red to another color, like blue. While there is no definite answer on how we perceive our surroundings, there is speculation by some experts on an association between perception and the pituitary gland.
But, what does that mean for perception? Does the pituitary play a role in the nature of perception? Let us find it out!
What Is Pituitary Gland?
Source: VectorStock
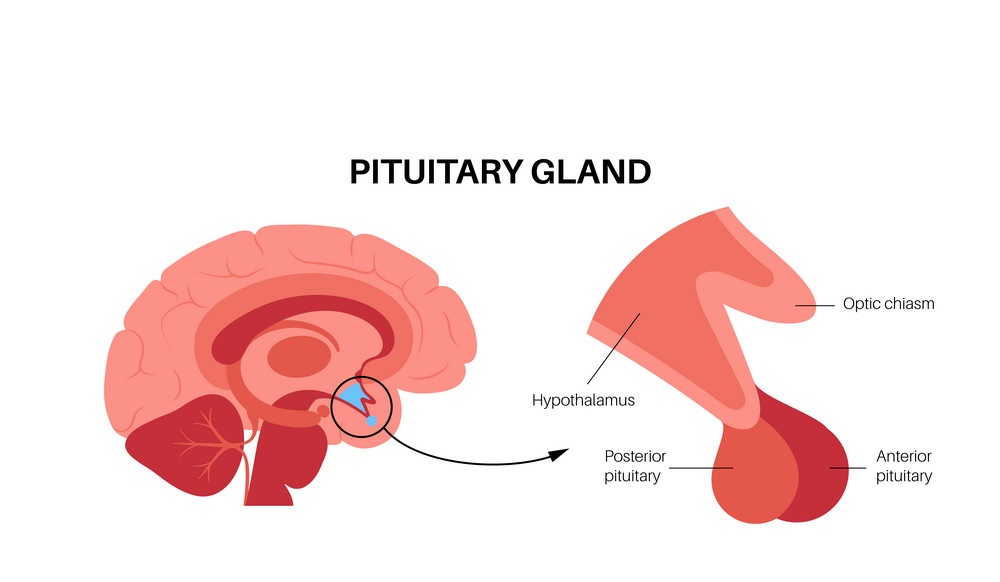
The pituitary gland is a small endocrine gland located in the center of the forehead, just above and between the eyes. The pituitary is part of the endocrine system, which includes hormones that are produced by glands and released into the bloodstream to control various body functions.
The pituitary gland is attached to the hypothalamus by an infundibulum (plural = infundibula). The hypothalamus regulates many body functions, including sleeping and waking cycles, thirst, hunger, and body temperature. It also produces hormones that regulate sexual development during puberty and reproductive functions throughout life.
What Are The Two Parts Of Pituitary Gland?
The pituitary gland is a very important part of the endocrine system. It has two parts:
Anterior Pituitary Gland
The anterior pituitary gland makes hormones that control the number of other hormones produced by other glands. For example, if you have an overactive thyroid gland (hyperthyroidism), your body will produce too much thyroid hormone. In this case, the anterior pituitary gland must produce less thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) so that the thyroid gland will stop making too much T4.
The anterior pituitary gland also produces adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) and luteinizing hormone (LH). ACTH stimulates the production of cortisol by the adrenal cortex, and LH stimulates ovulation in women and sperm production in men.
Source: Nagwa
Posterior Pituitary Gland
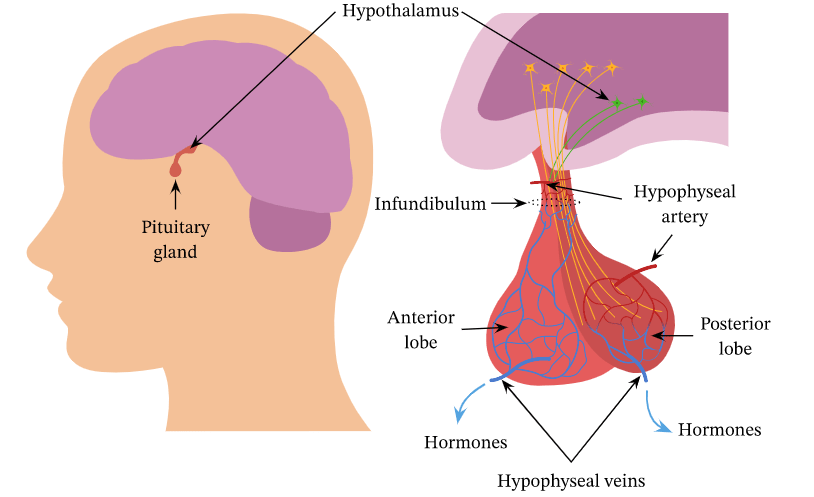
The posterior pituitary gland is also known as the neurohypophysis. It doesn’t make hormones itself; instead, it stores and releases hormones produced by the hypothalamus. These hormones are called oxytocin and vasopressin. The hypothalamus makes these hormones in response to a stimulus, such as when you eat or drink something cold. When the hormone enters the bloodstream, it travels to its target organ.
Oxytocin stimulates uterine contraction during childbirth, lactation (milk production), bonding between mother and child, and sexual arousal in both men and women. Vasopressin helps regulate water balance in the body by increasing urine production through increased blood pressure when fluid levels drop too low, or conversely by decreasing urine production when fluid levels rise too high (as with dehydration).
What Functions Does A Pituitary Gland Perform?
The pituitary gland receives messages from other parts of the brain and from hormones in the bloodstream. These messages tell it when to release its own hormones. The endocrine system uses hormones to communicate between different organs and tissues of the body.
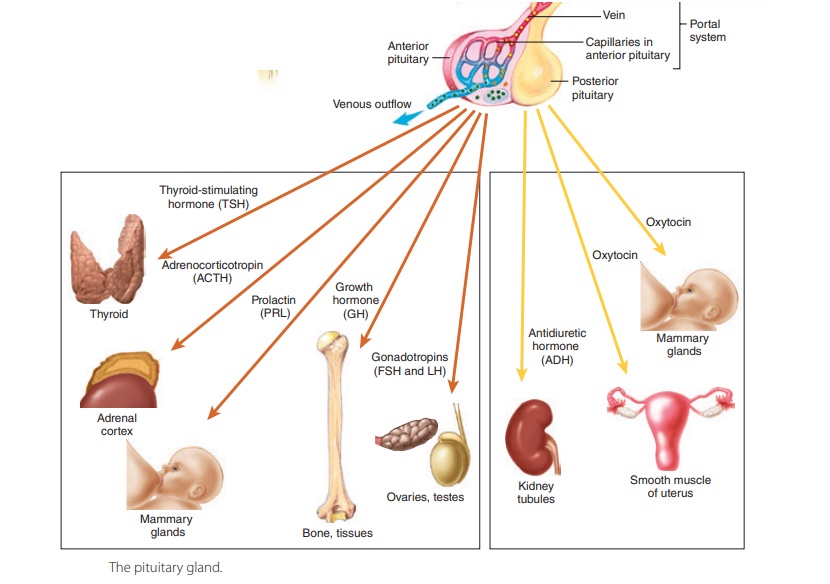
One of its main roles is to produce growth hormone and prolactin, which are important for normal growth in children and for lactation in women. The pituitary gland produces six hormones that control other glands in the body and regulate growth, metabolism, sexual function, pregnancy, and childbirth.
Source: Pharmacy180
The pituitary gland is divided into two sections: the anterior lobe and the posterior lobe. The anterior lobe produces hormones that affect the thyroid and adrenal glands (located near the kidneys), as well as growth hormones. The posterior lobe produces hormones that affect reproductive organs, including thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), and luteinizing hormone (LH).
The pituitary gland also produces growth factors that stimulate cell division and regulate blood pressure by controlling fluid retention in tissues.
Does The Pituitary Gland Play A Role In Perception?
The pituitary gland is the largest endocrine gland in the human body, weighing around 10 grams. It sits at the base of the brain, just above and behind the eyes. Because of its proximity to the optic chiasm, it has been suggested that it may also play a role in visual perception.

Source: MIT News
The studies that have been done on this subject have found some interesting results. For example, one study found that vision improves when looking at a picture of an object after receiving a dose of growth hormone or thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) from the pituitary gland. Another study showed that patients with damage to their pituitary glands were unable to match pictures of faces against pictures of houses and cars when asked to do so. This suggests that there may be some kind of connection between our sense of vision and our sense of smell, but more research is necessary before we can say for sure what this connection might be.
Oxytocin And Pituitary Gland
Oxytocin is a hormone produced in the hypothalamus and stored in the posterior pituitary gland. This hormone is also called the love hormone because it is released during hugging, touching, skin-to-skin contact, orgasm, and ejaculation.
Oxytocin is not only important for reproduction but also for lactation and the release of milk from the breasts. It has been shown that oxytocin can be released through skin contact as well as by kissing.
Source: Naturopathic Doctor News and Review
This hormone is also responsible for social bonding – especially between mother and child – as well as trust and empathy. It is thought that oxytocin may be one reason why mothers are so protective over their children since they release this hormone when they feel threatened or stressed out.
How Is Oxytocin Associated With Learning And Retention
Oxytocin has been shown to help with learning new information. In one study, researchers found that oxytocin improved memory retrieval in healthy men and women. The participants were given either oxytocin or a placebo before being asked to name pictures they had seen earlier in the study. The results showed that those who received oxytocin were more likely than those who did not correctly identify pictures they had seen previously.

Source: WeWork
Another study found that oxytocin boosts memory retention by increasing the activity of brain cells responsible for storing information. This suggests that oxytocin helps people learn new information better because it improves their ability to remember it later on when they need it most.
The effects of oxytocin on learning seem to be strongest when we are learning something new. In one study, volunteers who received oxytocin were better at learning a task that they had never performed before than they were at recalling information from memory. This suggests that oxytocin helps us form new memories more effectively than it helps us retrieve old ones.
How Does Perception Affect How We Interpret Our World?
Perception is the process by which we take in information from our environment and make sense of it. It is how we interpret everything from the color of a dress to the meaning behind a joke. And it is something we do all the time.
Sometimes, though, perception can lead us astray — especially when the way we see things conflicts with how others see them. This is called perceptual bias, and it happens for a variety of reasons.

For example:
We may be biased by our own experiences. People who have suffered from depression think other people are more depressed than they really are and that their problems are worse than other people’s problems (even if they are not).
We may be biased by our emotions and experiences with certain situations. For example, if you have had an unpleasant encounter with police officers in the past, you might perceive someone else’s behavior towards police officers as aggressive or hostile even if it isn’t meant that way at all (this is called “stereotype threat”).
We may also be biased by our personality type — whether we are more extroverted or introverted, neurotic or stable — which causes us to interpret situations differently than others might do so.
How Does The Mind Control How We Experience Events?
“The mind has a powerful impact on how we experience events,” writes neuroscientist David Eagleman in his new book, Incognito. “We are not passive recorders but active editors.”
Eagleman’s book explores the idea that our brains do much more than just passively receiving information from our senses. Instead, they actively construct what we perceive as reality.
In other words, your brain is a master storyteller. It does not just passively receive information from your senses and then interpret it — it actively constructs what you perceive as reality.

Source: Mindful.org
Cognitive scientist Daniel Kahneman calls this phenomenon “the illusion of insight.” When we make decisions about what to do in life or who to trust, for example, we often assume we have good reasons for those decisions. But if you ask people why they chose one option over another, they’re often unable to give a clear answer. Their brains simply constructed an explanation after the fact based on whatever information was available at the time — which is rarely enough for us to make truly rational decisions about anything.
The implications of this idea are profound. It means that there is no such thing as objective reality; everything is subjective because everything we experience is filtered through our brain’s interpretation.
Can The Pituitary And Other Glands Influence Our Perception Of Reality?
The pituitary gland influences our perception of reality by releasing hormones that affect our brains and bodies. These hormones are released in response to a variety of factors, such as stress, exercise, pregnancy, childbirth, and aging.
It has been said that when the pituitary gland is working properly, a person will have good mental clarity and be able to think clearly. If it isn’t functioning properly, however, then this may not be the case.
For example: if the hypothalamus gland is not secreting enough growth hormone, then this could affect your perception of reality by causing fatigue and weight gain as well as reducing your energy levels significantly.

Source: News Medical
What Can We Do To Alter Our Perception Of Reality?
The question of how we perceive reality is a big one. We are all aware that our perceptions are not reality. How do we change this?
In order to alter our perception of reality, we need to first understand what exactly is going on when we perceive something.
The first step in understanding this is by understanding that “things” do not exist outside of our minds. Everything that we experience is happening inside of our minds. This means that everything that we see, hear, smell, taste, and touch actually exists only as electrical signals in our brain. The brain then interprets these signals into something that makes sense to us.
So if we can not rely on our senses to tell us what is really going on around us, what does? Well, the answer lies in how the mind interprets these signals into images and other sensory experiences.

Source: VectorStock
Perception And Reality Are Not The Same Things
Our perception of reality is based on our beliefs about it. This means that if we believe something is true or real, then it will be real for us even though it may not be true at all! For example: if you think your boss is being unfair to you, then they will become an awful person who treats you badly at work because your mind will interpret their actions as being unfair. If, on the other hand, you believe your boss is being fair, then they will be a nice person who treats you well at work because of how your mind interprets their actions.
Conclusion & Takeaway
If you are able to extract anything at all from this small article, it is that the pituitary gland is a large structure that has supposedly been overlooked by medical science and helps to explain how we see, hear, taste, smell, and control our bodily functions. In other words, when it comes to how our bodies work and perhaps how we experience the world generally, the pituitary gland may play a far bigger role than what was previously believed.
Ultimately, the research is still inconclusive. But it’s good to know that this gland is still being studied.
If you want to learn more about the functions performed by the pituitary gland or about the disorders related to the pituitary gland, visit our website, Houston Endocrine Center.



Leave A Comment