
Source: Dexcom
What Is A Continuous Glucose Monitoring System (CGM)?
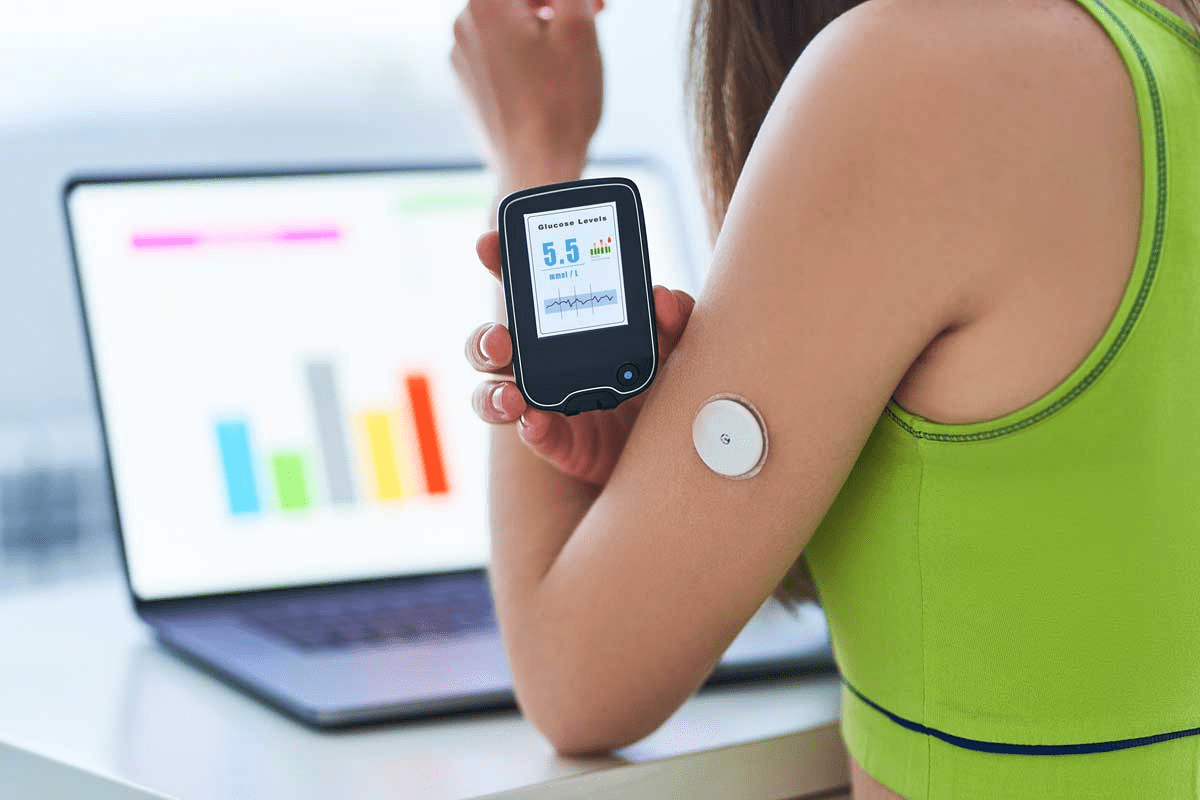
A Continuous Glucose Monitoring System (CGM) is a medical device that measures the patient’s blood sugar level. It does this by measuring the glucose levels in interstitial fluid, an important part of the body’s circulatory system.
CGMSs are typically used to monitor diabetes patients, but they can also monitor other diseases that cause high blood sugar levels. They are also used for research purposes and monitoring people with certain eating disorders.
A Continuous Glucose Monitoring device is inserted under the skin. It provides information on blood sugar levels. It measures glucose levels in the interstitial fluid, which can be used to detect patterns in insulin production and modify insulin doses accordingly.
A CGM can be inserted every day or as needed. It is typically worn for up to 14 days, but this duration may vary depending on the individual’s needs. The insertion site of a CGM can be changed if necessary. A CGM may also be removed at any time with no adverse effects.
The Use Of Continuous Glucose Monitoring System
A Continuous Glucose Monitoring System or CGM device helps manage diabetes. It monitors glucose levels and sends it to a device like a smartphone or a computer.
The continuous glucose monitor (CGM) tracks blood sugar levels in people with type 1 or type 2 diabetes. Blood sugar levels are monitored throughout the day and night, making it easier for people with diabetes to manage their condition. CGM also helps identify patterns of highs and lows, so people with diabetes can take appropriate action to prevent complications.
Continuous glucose monitors can be used in many ways, such as checking how long it takes for your pancreas to produce insulin after eating and monitoring how long it takes for your insulin levels to drop after taking insulin shots. They can also be used during exercise to measure how long it takes for your body’s cells to replenish their glucose supply.
Who Can Use Continuous Glucose Monitoring Devices?
The continuous glucose monitoring device is used by people with diabetes, those who have had a heart attack, and people with a high risk of developing diabetes.

Source: SingHealth
Both patients and healthcare providers use continuous glucose monitoring devices. Healthcare providers can use them to monitor patients for hyperglycemia, hypoglycemia, or other related conditions to blood sugar levels. Patients can use them to understand their health better and make more informed decisions about their lifestyles.
The uses of CGM devices are not limited to diabetics. It can be used by people with pre-diabetes, gestational diabetes, and those who are on insulin therapy for other conditions such as obesity and polycystic ovarian syndrome.
Why Should Diabetes Patients Measure Their Sugar?
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects the way your body processes sugar. It is caused by the pancreas not producing enough insulin or the body’s cells not responding to insulin.
A person with diabetes has either too much sugar (hyperglycemia) or too little sugar in their blood (hypoglycemia). In diabetes, high blood sugar levels are typically caused by two things:
– The body’s cells are not responding to insulin.
– The pancreas starts to make less and less insulin.
Monitoring blood sugar levels can help people with diabetes identify high and low blood sugar levels, which helps them make adjustments to their diet and exercise routine.

Source: Financial Times
There are various methods that a person can use to monitor their blood sugar levels, including the following:
A Blood Glucose Meter
A person uses this device to measure blood sugar levels. The glucose meter has a small vial inserted under the person’s tongue, and then the meter gives the person a reading of blood sugar level on a small digital display.
A Blood Sample
This can be taken from an arm vein, but it is more commonly taken from the fingertip or the inside of the person’s mouth. Special lancets are inserted into the skin and then a drop of blood is collected that is used to test blood sugar levels.
A Glucometer
This is a compact device also available at most drug stores. The glucometer has an insulin pen attached to it so that the person can get instant reading and make adjustments.
A Fingerstick
This method is done by pricking a person’s finger with a special lancet dipped in a tiny amount of blood-testing solution, is done by placing the lancet at the person’s fingertip and then pressing it.
A Urine Test
This testing method involves urinating into a small tube attached to a device that measures blood sugar levels.
Urine Test Strips
These strips are available at most drug stores. They come in a box of 100, but it may be more cost-effective to buy a larger box from the pharmacy. The test strip is dipped in the urine for five seconds and gives the results on a disposable paper card.
How Does CGM Work?
Continuous glucose monitors continuously measure blood glucose levels. These devices are more accurate than finger-prick testing and approved by the FDA for diabetes management. They are usually worn on the body and provide real-time readings.

Source: Maxim Integrated
The working of CGM is quite complex, but it involves an algorithm that analyzes the data from a sensor (usually a sensor inserted under the skin) to calculate the blood sugar level in real-time. The sensor sends data wirelessly to a receiver, which displays it on an LCD screen or prints it out for you. A transmitter sends this data wirelessly to a receiver connected to your PC, tablet, or smartphone. CGM works by measuring the amount of glucose in your blood through the sensor.
The transmitter tracks your glucose levels every five minutes. When glucose levels drop, the transmitter sends a message to your PC, tablet, or smartphone. You can then use the receiver or the software connected to it on your PC, tablet, or smartphone to display and log the data coming from CGM.

Source: NIDDK
The device also uses a predictive control algorithm, which uses information from previous blood sugar data and the user’s current behavior to predict future blood sugar levels. This process allows the device to deliver insulin or glucagon (a fast-acting glucose solution) and supplies a small amount of electrical energy when needed.
Difference Between CGM And Insulin Pumps
Continuous glucose monitors and insulin pumps have some similarities in their function. However, there are also some significant differences between them.
Continuous Glucose Monitors |
|---|
| People with diabetes often use continuous glucose monitors to monitor the glucose levels in their blood. |
| The monitor is attached to a finger or other part of the body, and it continuously measures blood sugar levels. |
| They can measure blood sugar levels as low as 20 mg/dl |
| They have alarms that sound if a person’s blood sugar is too high or too low |
| They are battery-powered and don’t need to be plugged in |
Insulin Pumps |
|---|
| The insulin pump delivers insulin through an infusion set into the body. |
| This can be done via a catheter or a cannula inserted under the skin. |
| They need to be plugged in |
| They can measure blood sugar levels through a catheter or a cannula that is inserted under the skin |
| They can be programmed to deliver a specific amount of insulin at a specified time |
Is It Easy To Use CGM Devices?
The answer is yes and no. Some people have a hard time understanding how to use the devices, but it is a good investment for those who do.
Some people may find it difficult to use CGM devices because they are unfamiliar with the technology or do not understand how it functions. They may think that CGM devices are too complicated and can’t be used by everyone. These people may be wrong because there are many ways to use these devices and many benefits associated with using them.
However, some people find it easy to use these devices and enjoy the benefits using them. They can successfully use a CGM device because they are familiar with the technology and understand how it works. This is especially true for people who already use insulin pumps and glucose meters.
Source: Rupa Health
The case of diabetes is often compared to the epidemic of obesity, and for a good reason. It is detrimental to the body not to control blood sugar levels. Controlling blood sugar levels through these devices enables people to manage their treatment plans with the proper tools personally.
CGM devices are beneficial because they allow people to monitor their blood sugar levels and adjust their treatment plans accordingly. These devices are often thought of as an alternative for people who do not require insulin or glucose meters to control blood sugar.
What Are The Advantages Of Using A Continuous Glucose Monitor System?
Continuous glucose monitors are taking the diabetes world by storm. Ease of use, accuracy, and convenience are just a few of the many advantages these devices have over traditional blood sugar monitoring methods.
Source: GluCare
The advantages of using a CGM system are many. They help in improving the quality of life;
- Providing more accurate data for diabetes management.
- Providing constant data streams.
- Preventing hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia.
- Monitoring ketones
- Managing blood sugar levels throughout the day.
- Reducing the number of fingerstick checks.
It is important to use technology to improve our lives to live healthier and happier lives in today’s world. Continuous glucose monitor systems are helping people live on their own terms while also following their health needs.
What Are The Disadvantages Of Using A Continuous Glucose Monitor System?
The use of CGM is not without its drawbacks. The main disadvantage of using a continuous glucose monitor system is the cost for the patient. The price ranges from $40 to $500 per month, and it can be difficult for some patients to afford this expense.
Some other disadvantages are:
- It’s not always accurate in predicting diabetes or hypoglycemia risk.
- It doesn’t take into account other factors such as insulin resistance, age, and body weight.
- It doesn’t provide information on how much insulin should be given;
- It isn’t portable.
- It can have challenges understanding the user’s glucose levels in their breath or other bodily fluids.
- The monitoring site doesn’t provide feedback on the type/amount of carbs/fat/protein consumed.
- It’s not a good idea for patients who want to maintain a low-calorie diet.
- There are no model-specific comparisons of one brand’s accuracy and reliability rates vs. another brand.
Additionally, the CGM does not provide information on trends and patterns in blood sugar levels.
The Cost Of Continuous Glucose Monitoring Devices
Continuous glucose monitoring devices is becoming more popular as technology improves. It is not just the cost that makes CGM devices expensive but also that they need to be replaced every year.
The American Diabetes Association recommends that people with type 2 diabetes start using a continuous glucose monitoring device within three to six months of diagnosis. They also recommend that people with type 1 diabetes use this device after two years of diagnosis.
The cost of a continuous glucose monitoring device can vary depending on its features and brand, but it is estimated to be anywhere from $100 to $500 per year.
Some people may argue that CGM devices are expensive, but it becomes a lot more affordable if you consider the time saved in managing diabetes. The cost of CGM devices is comparable to other medical devices. However, the cost of a CGM device lessens over time as new models come out with lower prices and improved features.
Some insurance policies cover the costs of insulin pumps or CGMs, so it may be beneficial to check your coverage. Additionally, it’s important to remember that this device can be used for an unlimited time, so the ongoing costs are significantly lower.
However, the cost of a continuous glucose monitoring device is not the only thing that needs to be considered when managing diabetes. Other factors such as time and effort required, patient compliance, and any potential side effects need to be considered before deciding whether or not this device is worth it.
Is A Fingerstick Check Required When Using A CGM Device?
A fingerstick check is a blood test usually done before using a CGM device. It is done to ensure that the blood sugar levels are within the normal range.
The fingerstick check helps ensure that the patient has not developed any complications with their diabetes while using their CGM device. However, some people have an allergy to lancets, and they may have reactions when they use them.

Source: GettyImages
Fingerstick checks are only required when using a CGM device for the first time or if it has been more than 24 hours since the last test. The fingerstick check aims to ensure that the patient’s CGM readings are accurate and detect any changes in the patient’s condition.
Fingerstick checks are not required for patients who use insulin pumps or continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion (CSII) devices.
Where To Get A CGM From?
Different types of CGM devices are available in the market. The selection process is a little tricky. It would help if you considered budget, location, and device type.
There are three main types of CGM devices:
- Continuous glucose monitors
- Insulin pumps
- Continuous blood glucose monitors.
Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGM)
They use a sensor to measure the amount of sugar in a person’s blood over time. People with diabetes can use them to track their blood sugar levels throughout the day and night.
Insulin Pumps
Unlike CGM devices, insulin pumps deliver an insulin infusion through a catheter inserted under the skin that a remote computer may regulate. This allows insulin to be delivered without waiting for the body’s natural release of glucose. Insulin pumps can also help some people achieve and maintain near-normal blood sugar levels.
Continuous Blood Glucose Monitors (CBG)
They use sensors to measure the amount of sugar in a person’s blood over time. Still, they also measure other things like hemoglobin A1c or ketone levels if someone has diabetes or is on a ketogenic diet.
If you face any issues finding the best CGM system, you can visit Houston Endocrine Center and book an appointment with us to avail our services.



Leave A Comment